
Understanding Double-Hung Window Parts: A Comprehensive Guide
Enhancing aesthetics and functionality, double-hung windows have been a popular choice in architecture for centuries. The classic design offers versatility and complements various architectural styles, making them a favorite among homeowners. If you're curious about the inner workings of these charming windows, join us as we explore the 12 essential parts of double-hung windows.

-
Sash:
The sash is the movable part of the window that holds the glass panes. Double-hung windows have two sashes, the upper and lower, which can move independently. The ability to move the sashes allows for easy ventilation and cleaning.

-
Rails:
Rails are horizontal components that run along the top and bottom edges of each sash. They play a crucial role in supporting the sash and allowing it to slide up and down within the window frame.

-
Stiles:
Stiles are the vertical components on the sides of the sashes. They provide structural support and stability to the window. The stiles also contain the mechanisms that enable the sashes to move smoothly.

-
Meeting Rail:
The meeting rail is the horizontal bar where the upper and lower sashes meet when the window is closed. It forms a tight seal to prevent air and water from entering the interior, enhancing energy efficiency and weather resistance.

-
Sash Locks:
Sash locks are mechanisms located at the meeting rail that secure the two sashes together when the window is closed. They ensure a tight seal and improve security by preventing unauthorized access from the outside.
-
Balances:
Traditional double-hung windows are counterweighted, using two window balances concealed within the window frame. The weight of the balances help offset the sash's weight, making it easier to open and close the window.
-
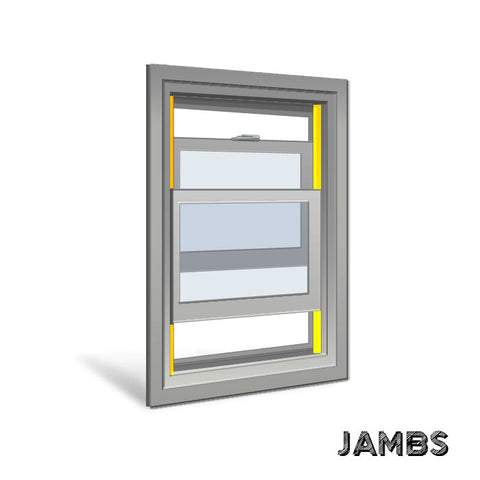
Jambs:
The jambs are the vertical components of the window frame that surround the sashes. They provide structural integrity and space for the sashes to slide up and down.

-
Casing:
The casing is the visible trim that surrounds the window on the interior side. It enhances the aesthetics of the window and covers the gap between the window frame and the wall, giving it a finished look.

-
Sill:
The sill is the horizontal component at the bottom of the window frame. It provides support to the lower sash when it is in the closed position and helps to shed water away from the interior.

-
Sash Lifts:
Sash lifts are small handles or pulls installed on the bottom rail of the lower sash. They allow for easy and secure operation when opening and closing the lower sash.
-
Check Rails:
Check rails are located on both sashes and serve as a stopping point when the window is closed. They help maintain alignment and prevent drafts between the sashes.

-
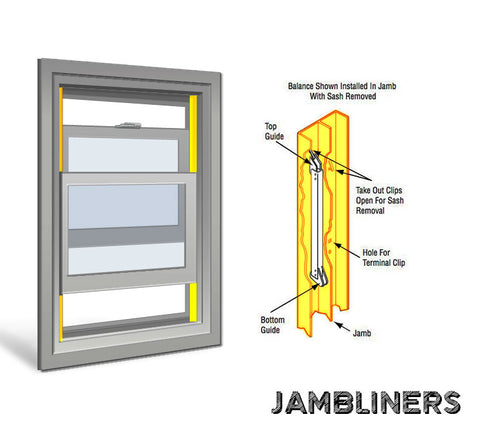
Jamb Liners:
In modern double-hung windows, jamb liners are often used instead of traditional window balances. Jamb liners contain the window balances to aid in the smooth movement of the sashes.
Conclusion
Understanding the various parts of double-hung windows not only enriches your knowledge of architecture but also empowers you to make informed decisions when maintaining, repairing, or replacing these windows. Whether you are preserving the historic charm of an old home or seeking to enhance the beauty of a new one, double-hung windows offer timeless elegance and functionality that continues to withstand the test of time. Still have questions about double-hung window parts? Contact the WHD Team! We’ve got experts ready to give you answers.



